The Aging Process
The aging process is a complex, multifaceted phenomenon that affects every living organism,including humans. It is characterized by a gradual decline in physiological functions,
increased susceptibility to disease, and a reduced capacity for adaptation. Aging is not a
singular event but a continuous process that begins at birth and unfolds over time.
At the cellular level, aging involves a variety of changes. Telomere shortening, the
progressive loss of protective caps on the ends of chromosomes, contributes to cellular
senescence, where cells lose their ability to divide. Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance
between free radicals and antioxidants, damages cellular components like DNA and proteins.
Changes in gene expression and epigenetic modifications also play a role in regulating the
aging process.
Time to feel better. Find a mental, physical health expert that works for you.
Organ systems undergo significant changes with age. The cardiovascular system experiences
stiffening of arteries, decreased cardiac output, and increased risk of hypertension and heart
disease. The respiratory system shows reduced lung capacity and decreased efficiency of gas
exchange. The musculoskeletal system loses muscle mass and bone density, leading to frailty
and increased risk of fractures. The immune system weakens, making individuals more
susceptible to infections and autoimmune diseases.
Hormonal changes are another hallmark of aging. Menopause in women and andropause in
men lead to significant shifts in hormone levels, affecting reproductive function, bone health,
and mood. The endocrine system as a whole experiences changes in hormone production and
sensitivity, contributing to metabolic disorders and other age-related conditions.
Environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and genetic predispositions interact to influence the
rate and pattern of aging. Exposure to toxins, chronic stress, poor diet, and lack of physical
activity can accelerate aging. Conversely, healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise, a
balanced diet, and stress management, can promote healthy aging.
The aging process is also accompanied by psychological and social changes. Individuals may
experience changes in cognitive function, emotional regulation, and social roles. Adapting to
these changes and maintaining a sense of purpose and social connection are essential for
successful aging.
Understanding the aging process is crucial for developing interventions to promote healthy
aging and prevent age-related diseases. Research in gerontology continues to advance our
knowledge of the biological, psychological, and social aspects of aging, paving the way for
improved quality of life in later years.
Brain Changes in Aging
The aging brain undergoes a variety of structural and functional changes that can affect
cognitive abilities and overall well-being. While some changes are inevitable, others can be
mitigated through lifestyle choices and interventions.
One of the most noticeable changes is a decrease in brain volume, particularly in the
prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. The prefrontal cortex, responsible for executive functions
like planning and decision-making, shows a decline in gray matter volume, leading to
reduced cognitive flexibility and working memory. The hippocampus, crucial for memory
formation, also experiences shrinkage, contributing to age-related memory decline.
Neurotransmitter systems undergo changes with age. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved
in reward and motivation, shows a decline in production and receptor sensitivity, affecting
motor control and mood. Serotonin, which regulates mood and sleep, also experiences
changes, contributing to increased risk of depression and sleep disturbances.
White matter, the connective tissue that facilitates communication between brain regions,
also experiences changes. White matter integrity declines with age, leading to slower
processing speed and reduced cognitive efficiency.
Cognitive functions are affected by these brain changes. Memory, particularly episodic
memory (memory of specific events), tends to decline with age. Processing speed, the ability
to rapidly process information, also slows down. However, other cognitive functions, such as
crystallized intelligence (accumulated knowledge and skills), may remain stable or even
improve with age.
Neuroplasticity, the brain ability to reorganize itself, remains present in the aging brain,
although it may be reduced compared to younger brains. Engaging in mentally stimulating
activities, such as learning new skills, solving puzzles, and social interaction, can promote
neuroplasticity and maintain cognitive function.
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in brain aging. Regular physical exercise, a balanced diet,
stress management, and adequate sleep can promote brain health and mitigate age-related
cognitive decline. Managing chronic conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes, is also
essential for maintaining brain health.
Research in neuroscience continues to advance our understanding of brain aging and develop
interventions to promote cognitive health. Early detection of cognitive decline and
personalized interventions can help individuals maintain cognitive function and quality of life
in later years.
Successful Aging
Successful aging is a concept that emphasizes maintaining physical, cognitive, and social
well-being in later life. It about maximizing one potential and quality of life, rather than
simply avoiding disease or disability. Successful aging involves a proactive approach to
health and well-being, encompassing lifestyle choices, psychological resilience, and social
engagement.
Physical activity is a cornerstone of successful aging. Regular exercise, including aerobic
exercise, strength training, and balance exercises, helps maintain muscle mass, bone density,
and cardiovascular health. It also improves mood, cognitive function, and overall quality of
life.
A balanced diet is essential for supporting physical and cognitive health. Consuming nutrient-
rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, provides the body with
the necessary nutrients for optimal functioning. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and
excessive alcohol intake is also important.
Cognitive stimulation is crucial for maintaining brain health. Engaging in mentally
challenging activities, such as learning new skills, solving puzzles, and reading, helps
promote neuroplasticity and cognitive function. Social engagement also plays a vital role.
Maintaining meaningful relationships, participating in social activities, and volunteering can
enhance well-being and reduce feelings of isolation.
Psychological resilience is another key aspect of successful aging. Developing coping
mechanisms for stress, maintaining a positive attitude, and finding meaning and purpose in
life can help individuals navigate the challenges of aging. Mindfulness and meditation
practices can also promote emotional well-being.
Preventive healthcare is essential for maintaining physical and cognitive health. Regular
check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations can help detect and manage chronic conditions.
Managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use are
also important.
Successful aging is not just about individual choices; it also requires supportive
environments. Access to healthcare, social services, and community resources can help
individuals maintain their independence and quality of life.
Ultimately, successful aging is a holistic approach that integrates physical, cognitive, and
social well-being. It’s about embracing the opportunities and challenges of later life and
maintaining a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
Connect Free. Improve your mental and physical health with a professional near you

Biological Aging
Biological aging is a complex process characterized by the gradual deterioration of
physiological functions over time. It not a single event but a progressive accumulation of
molecular and cellular damage that leads to organ system decline and increased vulnerability
to disease. Several key mechanisms contribute to biological aging.
Telomere shortening is a primary driver. Telomeres, protective caps on the ends of
chromosomes, shorten with each cell division. When telomeres become critically short, cells
enter senescence, losing their ability to divide. This contributes to tissue aging and organ
dysfunction.
Oxidative stress, caused by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, damages
cellular components like DNA, proteins, and lipids. Free radicals, unstable molecules
produced during normal metabolism, can cause significant cellular damage if not neutralized
by antioxidants. This cumulative damage contributes to aging and age-related diseases.
Inflammation, particularly chronic low-grade inflammation, plays a significant role.
Inflammaging, the persistent low-grade inflammation associated with aging, contributes to
various age-related diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and
neurodegenerative disorders.
Changes in protein homeostasis, the balance between protein synthesis and degradation, are
also crucial. With age, protein misfolding and aggregation increase, leading to cellular
dysfunction. This is particularly relevant in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer and
Parkinson.
Mitochondrial dysfunction, the powerhouses of cells, also contributes to aging. Mitochondria
produce energy (ATP), but with age, their function declines, leading to reduced energy
production and increased production of free radicals.
Changes in the endocrine system, the system of hormone-producing glands, are another
significant aspect. Hormonal changes, such as menopause in women and andropause in men,
affect various physiological processes, including metabolism, bone health, and mood.
Genetic factors play a role in determining the rate of biological aging. Certain genes are
associated with longevity and healthy aging, while others are associated with increased risk
of age-related diseases.
Understanding the mechanisms of biological aging is essential for developing interventions to
promote healthy aging and prevent age-related diseases. Research in gerontology continues to
advance our knowledge of these mechanisms, paving the way for improved quality of life in
later years.
Aging and Mental Wellness
Aging brings about significant changes that can impact mental wellness. While some
individuals experience robust mental health in later life, others may face challenges such as
depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. Understanding the interplay between aging and
mental wellness is crucial for promoting healthy aging.
Depression is a common mental health issue among older adults. It can manifest as persistent
sadness, loss of interest in activities, and changes in sleep and appetite. Depression in older
adults is often underdiagnosed and undertreated, highlighting the need for increased
awareness and screening.
Anxiety disorders are also prevalent. Older adults may experience anxiety related to health
concerns, financial worries, or social isolation. Generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder,
and social anxiety disorder can significantly impact quality of life.
Cognitive decline, including memory loss and reduced cognitive function, is a major concern.
While some cognitive changes are a normal part of aging, others may indicate mild cognitive
impairment or dementia. Early detection and intervention are essential for managing
cognitive decline.
Social isolation and loneliness can have a significant impact on mental wellness. Older adults
who lack social support are at increased risk of depression and cognitive decline. Maintaining
meaningful relationships and participating in social activities are crucial for promoting
mental wellness.
Physical health conditions can also affect mental wellness. Chronic illnesses, such as heart
disease, diabetes, and arthritis, can lead to pain, disability, and emotional distress. Managing
these conditions and promoting physical activity can improve mental wellness.
Access to mental health services is essential for older adults. However, stigma, lack of
awareness, and limited access to care can create barriers. Promoting mental health literacy
and providing accessible mental health services are crucial.
Promoting resilience and coping skills can help older adults navigate the challenges of aging.
This includes developing positive coping mechanisms, engaging in enjoyable activities, and
practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
Creating supportive environments is also crucial. This involves fostering social connections,
providing access to resources, and promoting a sense of purpose and belonging. Recognizing
and addressing the mental wellness needs of older adults is essential for promoting healthy
and fulfilling aging.
Elder Care
Elder care encompasses a range of services and support designed to meet the physical,
emotional, and social needs of older adults. It's a multifaceted area that addresses the diverse
needs of an aging population. Effective elder care is crucial for promoting quality of life and
maintaining independence in later years.
Home care services are a common form of elder care. These services provide assistance with
activities of daily living (ADLs), such as bathing, dressing, and meal preparation, in the
individual home. Home care can also include medication management, transportation, and
companionship.
Adult day care centers offer a structured environment for older adults to participate in social
activities, receive meals, and access healthcare services. These centers provide respite for
caregivers and promote social engagement for older adults.
Assisted living facilities provide a residential setting with varying levels of care. These
facilities offer assistance with ADLs, meals, and social activities, while promoting
independence and privacy. Assisted living is suitable for individuals who need some support
but do not require 24-hour medical care.
Nursing homes provide 24-hour medical care and support for individuals with complex health
needs. These facilities offer skilled nursing care, rehabilitation services, and assistance with
ADLs. Nursing homes are suitable for individuals who require intensive medical care and
support.
Respite care provides temporary relief for caregivers. This can include short-term stays in
assisted living facilities or nursing homes, or in-home care services. Respite care allows
caregivers to take breaks and recharge.
Hospice care provides end-of-life care for individuals with terminal illnesses. This includes
pain management, emotional support, and spiritual care. Hospice care can be provided in the
individual's home, a hospice facility, or a hospital.
Financial planning is an essential aspect of elder care. Long-term care costs can be
significant, and it's important to plan for these expenses. This may involve long-term care
insurance, savings, or government assistance programs.
Caregiver support is crucial. Caring for an older adult can be physically and emotionally
demanding. Caregivers need access to resources, support groups, and respite care to maintain
their own well-being.
Effective elder care requires a person-centered approach that focuses on the individual
needs and preferences. This includes promoting autonomy, dignity, and quality of life.
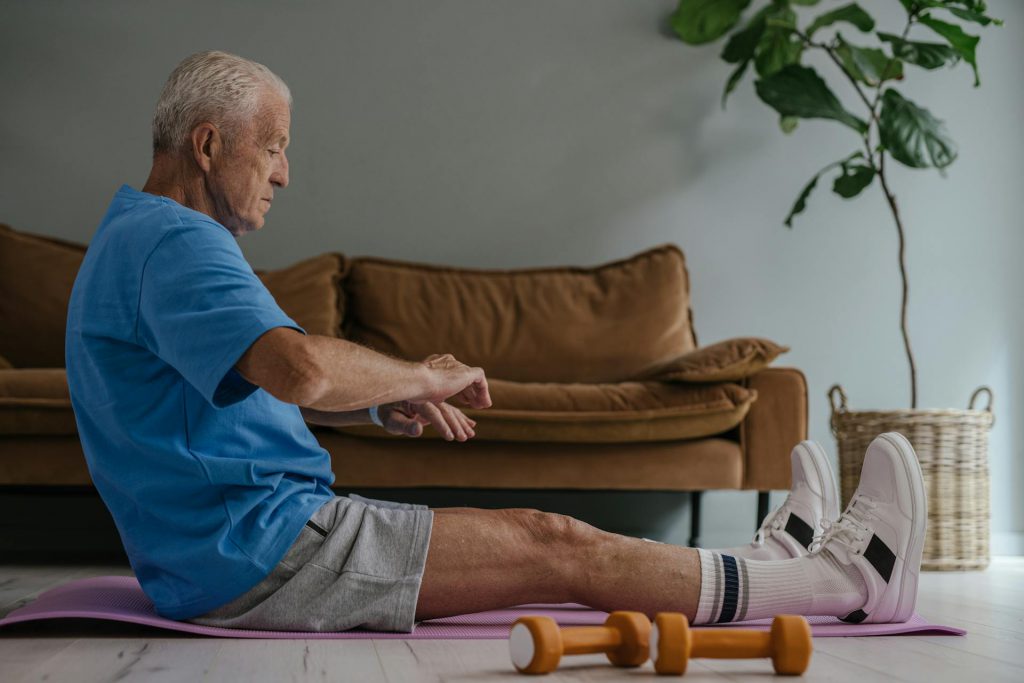
Benefits of Aging
While aging is often associated with decline, it also brings a wealth of benefits that enhance
quality of life and personal growth. These benefits are often overlooked but are essential for
promoting positive aging.
Wisdom and experience are significant benefits. Older adults have accumulated a lifetime of
knowledge, skills, and insights. This wisdom can be invaluable in problem-solving, decision-
making, and providing guidance to younger generations.
Emotional regulation often improves with age. Older adults tend to be better at managing
their emotions and maintaining a positive outlook. This emotional stability can enhance
relationships and overall well-being.
Increased self-awareness and self-acceptance are common benefits. Older adults often have a
clearer understanding of their strengths, weaknesses, and values. This self-awareness can lead
to greater contentment and peace of mind.
Stronger social connections can be a benefit. Older adults often have more time to nurture
relationships with family and friends. These social connections can provide emotional
support and reduce feelings of isolation.
Increased appreciation for life is a common benefit. Older adults often have a greater
appreciation for the simple joys of life, such as spending time with loved ones, enjoying
nature, or pursuing hobbies.
Reduced stress and anxiety are often experienced. Older adults may have fewer
responsibilities and less pressure, leading to a more relaxed and peaceful lifestyle.
Greater sense of purpose and fulfillment can be found. Older adults may have more time to
pursue their passions, volunteer, or engage in meaningful activities that contribute to their
sense of purpose.
Increased creativity and artistic expression can occur. Older adults may have more time to
explore their creative side, whether through painting, writing, music, or other artistic pursuits.
A stronger sense of community can be developed. Older adults may have more time to
participate in community activities and build relationships with their neighbors.
Ultimately, aging can bring a wealth of benefits that enhance quality of life and personal
growth. By recognizing and embracing these benefits, older adults can live fulfilling and
meaningful lives.

Free consultations. Connect free with local health professionals near you.
Conclusion
The journey of aging is a complex interplay of biological processes, mental wellness,
caregiving, and personal growth. Biological aging, marked by cellular and systemic changes,
underscores the importance of healthy lifestyles. Brain changes in aging, while presenting
challenges, can be mitigated through cognitive stimulation and proactive health management.
Successful aging emphasizes maintaining physical, cognitive, and social well-being,
highlighting the value of resilience and engagement. Aging and mental wellness are
intricately linked, necessitating awareness and accessible mental health services. Elder care
encompasses diverse services, from home care to hospice, emphasizing person-centered
approaches and caregiver support. Importantly, aging brings numerous benefits, including
wisdom, emotional regulation, and enhanced appreciation for life. By understanding and
addressing the challenges, and embracing the advantages, individuals can navigate aging with
dignity and fulfillment.
Time to feel better. Find a mental, physical health expert that works for you.
Common FAQs
What are the main biological changes that occur during aging?
Main changes include telomere shortening, oxidative stress, inflammation, mitochondrial
dysfunction, and hormonal shifts.
How can I maintain brain health as I age?
What is successful aging?
What mental health issues are common in older adults?
How can I help an aging loved one with their mental health?
What types of elder care services are available?
How can I plan for the financial costs of elder care?
What are some benefits of aging?
How can I promote healthy aging?
What is the role of genetics in aging?
People also ask
Q: Is it ageing or aging?
Q:What do you mean by aging?
Aging is the process of growing older, involving physical, emotional, and mental changes that occur over time. It can also refer to the deterioration of physiological functions or the intentional creation of an aged appearance in art, objects, or even financial accounts.
Q: What are the 4 types of aging?
Q:What is aging my face?
NOTICE TO USERS
MindBodyToday is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice, diagnosis, medical treatment, or therapy. Always seek the advice of your physician or qualified mental health provider with any questions you may have regarding any mental health symptom or medical condition. Never disregard professional psychological or medical advice nor delay in seeking professional advice or treatment because of something you have read on MindBodyToday.
Share this article

Let us know about your needs
Quickly reach the right healthcare Pro

Message health care pros and get the help you need.
Popular Healthcare Professionals Near You
You might also like
What is Family Systems Therapy: A…
, What is Family Systems Therapy? Everything you need to know Find a Pro Family Systems Therapy: Understanding the Individual […]
What is Synthesis of Acceptance and…
, What is Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)? Everything you need to know Find a Pro Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Synthesizing […]
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)…
, What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy ? Everything you need to know Find a Pro Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Theoretical Foundations, […]





